Abstract
Mechanical reasoning is a hallmark of human intelligence, defined by its ubiquitous yet irreplaceable role in human activities ranging from routine tasks to civil engineering. Embedding machines with mechanical reasoning is therefore an important step towards building human-level artificial intelligence.
Here, we leveraged 155 cognitive experiments to test the understanding of system stability, gears and pulley systems, leverage principle, inertia and motion, and fluid mechanics in 26 Vision Language Models (VLMs). Results indicate that VLMs consistently perform worse than humans on all domains, while demonstrate significant difficulty in reasoning about gear systems and fluid mechanics. Notably, their performance on these tasks do not improve as number of parameters increase, suggesting that current attention-based architecture may fail to grasp certain underlying mechanisms required for mechanical reasoning, particularly those pertaining to mental simulations.
Introduction
Humans are uniquely capable of working with complex mechanical systems, ranging from routine tasks, such as assembling furniture, to large-scale civil endeavors, such as designing architectural structures and developing advanced technologies. These capabilities are underpinned by the cognitive ability to reason about the relationships and interactions of physical objects, an ability known as mechanical reasoning.
While mechanical reasoning is a high-level cognitive ability that does not emerge until late childhood, it has been found to rely heavily on more foundational cognitive strategies. In particular, decades of research in cognitive science suggest that mental simulation, the process of constructing and operating mental models of the world to guide reasoning, is critical for many aspects of mechanical reasoning.
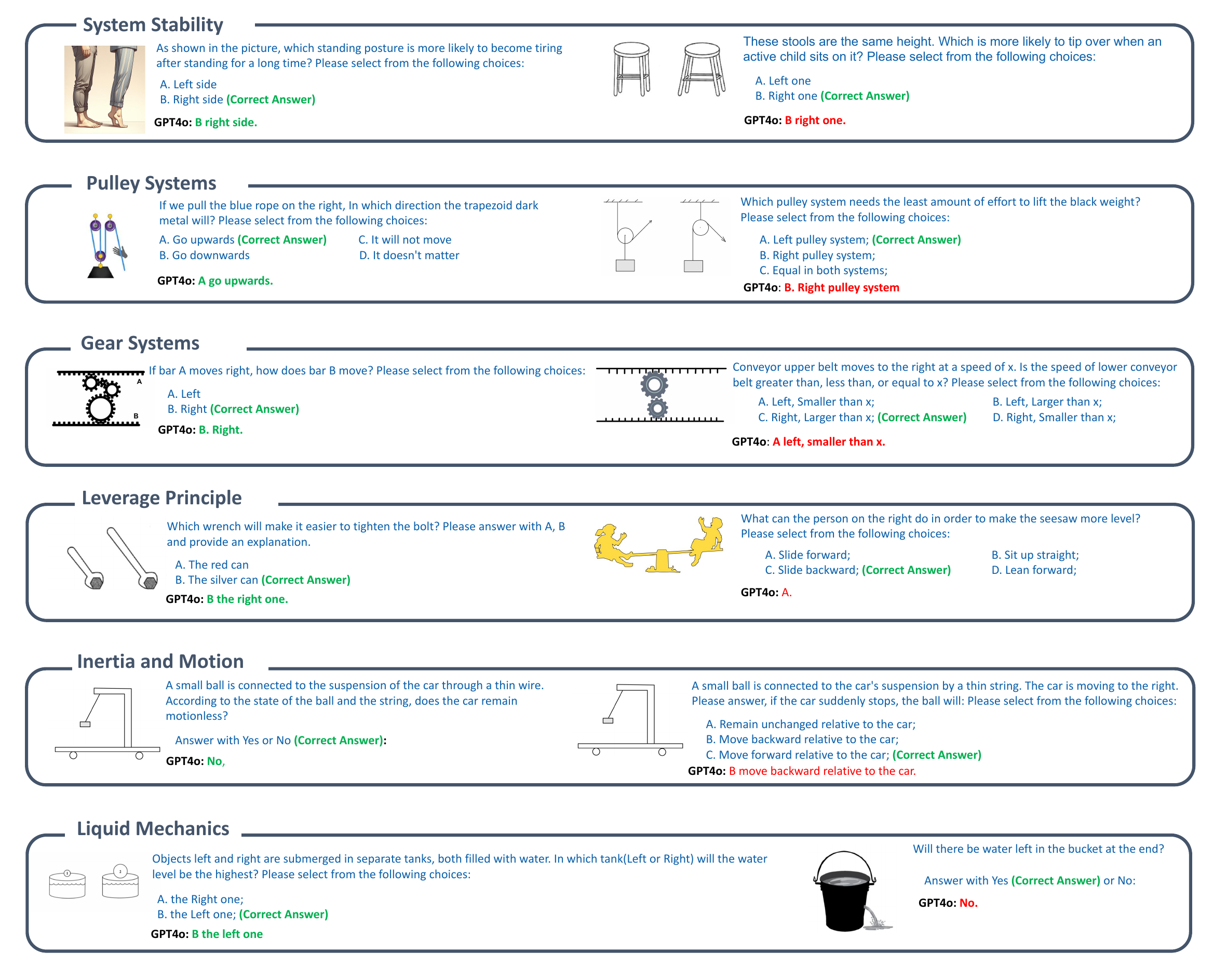 Sample tasks on the six domains of MechBench. For each domain, GPT4o answered correctly to the task on the left and failed the task on the right.
Sample tasks on the six domains of MechBench. For each domain, GPT4o answered correctly to the task on the left and failed the task on the right.
MechBench: A Benchmark for Mechanical Reasoning
To systematically evaluate VLMs' mechanical reasoning abilities, we constructed the MechBench, which contains around 155 cognitive experiments. The experiments investigate six generalized domains of mechanical reasoning:
System Stability
The understanding of stability is essential for reasoning about states of equilibrium within physical systems, such as predicting whether a stack of blocks will remain upright or collapse. In our experiments, models are presented with images of objects like stools with varying base widths or angles of inclination. The task involves selecting the most stable configuration.
 VLMs' performance on reasoning about mechanical system stability. Models excel at identifying objects and their mechanical states, but often fail to make correct stability predictions.
VLMs' performance on reasoning about mechanical system stability. Models excel at identifying objects and their mechanical states, but often fail to make correct stability predictions.
Pulley Systems
Pulley systems are widely used in cognitive psychology and physics education to study how individuals reason about force and motion, requiring an understanding of force distribution and machinery functions. For example, a simple task might involve determining which pulley system requires less effort to lift a weight.
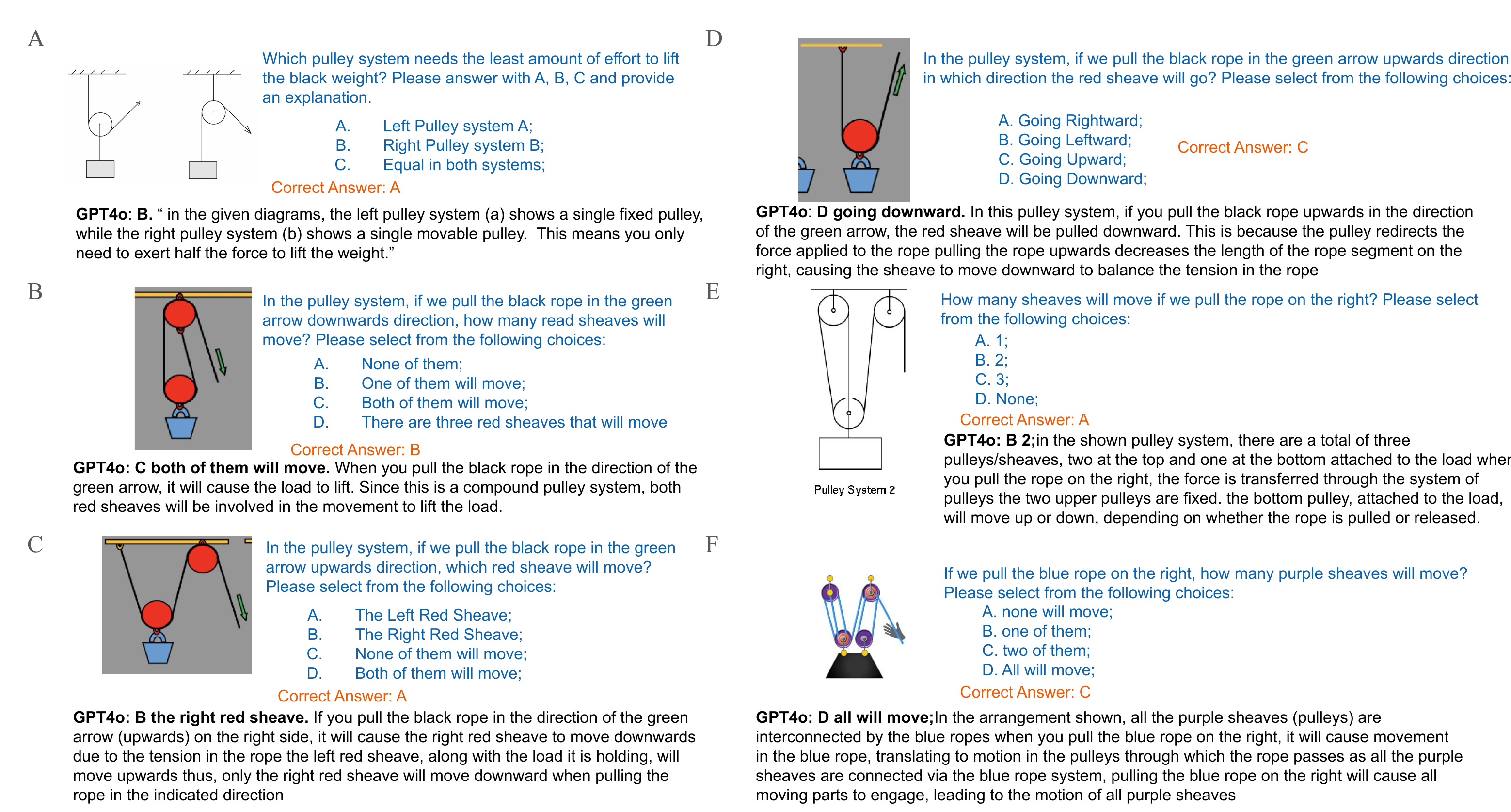 VLMs struggle with pulley systems in two main ways: they cannot consistently identify movable pulleys, and they have difficulty predicting whether objects will rise or fall in pulley systems.
VLMs struggle with pulley systems in two main ways: they cannot consistently identify movable pulleys, and they have difficulty predicting whether objects will rise or fall in pulley systems.
Gear Systems
Gear systems are deterministic mechanical setups governed by well-defined rules, such as adjacent gears rotating in opposite directions and gear ratios determining relative speeds. These properties make gears an ideal domain for testing logical and causal reasoning. Tasks in this category involve analyzing diagrams of connected gears to predict their rotational direction and speed.
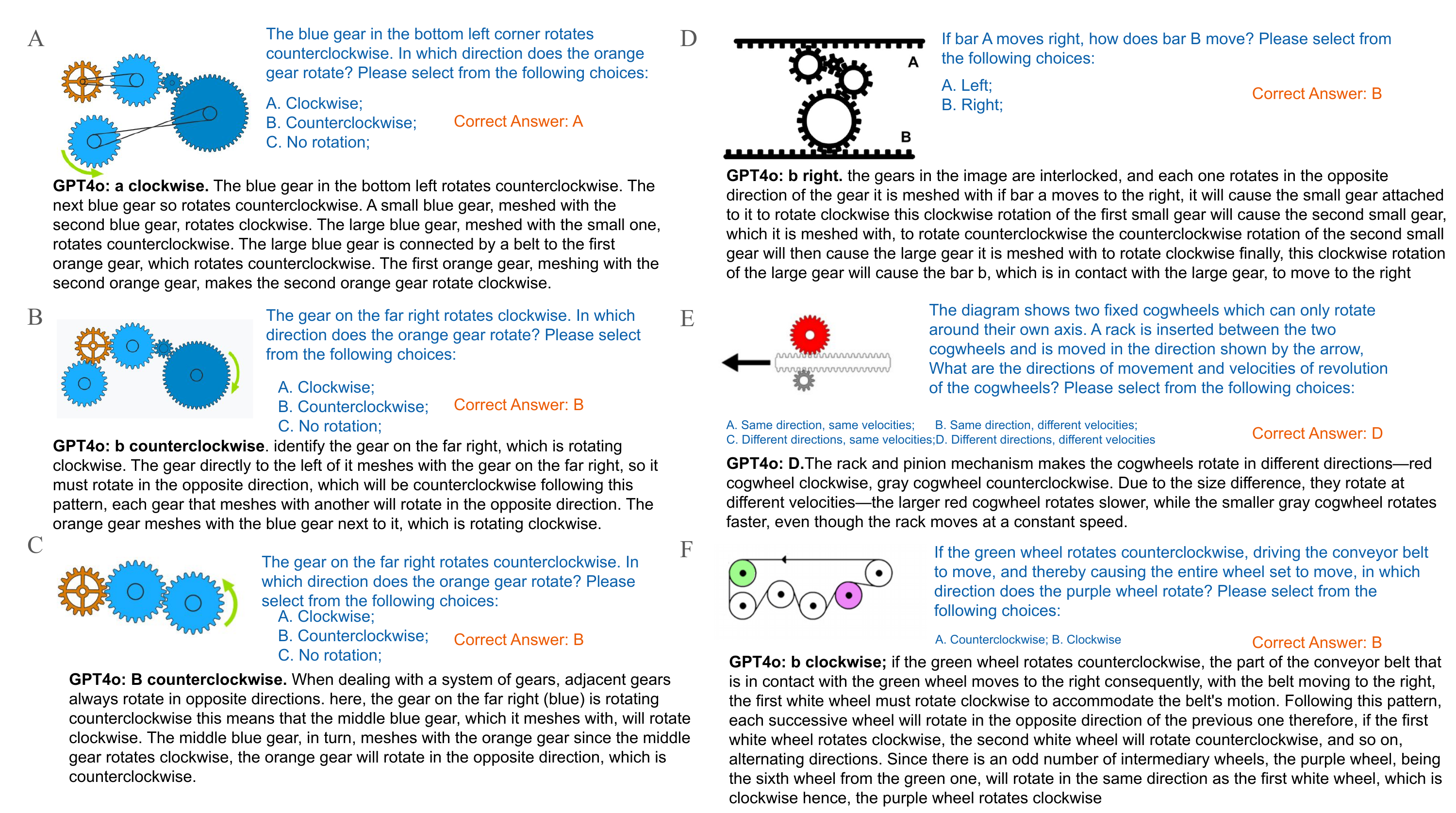 On gear and conveyor belt problems, VLMs are able to give highly accurate judgments. They can reliably determine the rotation of one pulley based on the direction of another.
On gear and conveyor belt problems, VLMs are able to give highly accurate judgments. They can reliably determine the rotation of one pulley based on the direction of another.
Leverage Principle
The leverage principle illustrates the relationship between force, distance, and torque. Balance-scale experiments in cognitive psychology have shown how humans progressively develop an understanding of leverage through iterative learning and application. Tasks in this category include determining how shifting weights on a seesaw or applying force to a lever affects balance.
 VLMs show diverse behaviors when solving seesaw-like mechanical systems. They excel at simple question-answering and basic extrapolations, but struggle with multi-step reasoning processes.
VLMs show diverse behaviors when solving seesaw-like mechanical systems. They excel at simple question-answering and basic extrapolations, but struggle with multi-step reasoning processes.
Inertia and Motion
Inertia and motion are dynamic aspects of mechanical reasoning that require understanding how forces influence the movement of objects over time. These concepts are central to Newtonian mechanics and intuitive physics. Human cognition integrates spatial and temporal information to make predictions about motion and forces, as seen in studies of tool use and physical reasoning.
 VLMs can identify mechanical situations but often lack the ability to effectively predict the next step based on the current scene, especially for complex inertia and motion problems.
VLMs can identify mechanical situations but often lack the ability to effectively predict the next step based on the current scene, especially for complex inertia and motion problems.
Fluid Mechanics
Fluid mechanics involves understanding the behavior of liquids under various conditions, such as flow, external pressures, and volume changes. Although grounded in the intuitive understanding of fluid dynamics that emerges very early in humans' cognitive development, reasoning about liquid behaviors in mechanical systems requires simultaneous consideration of geometry, force, and dynamics.
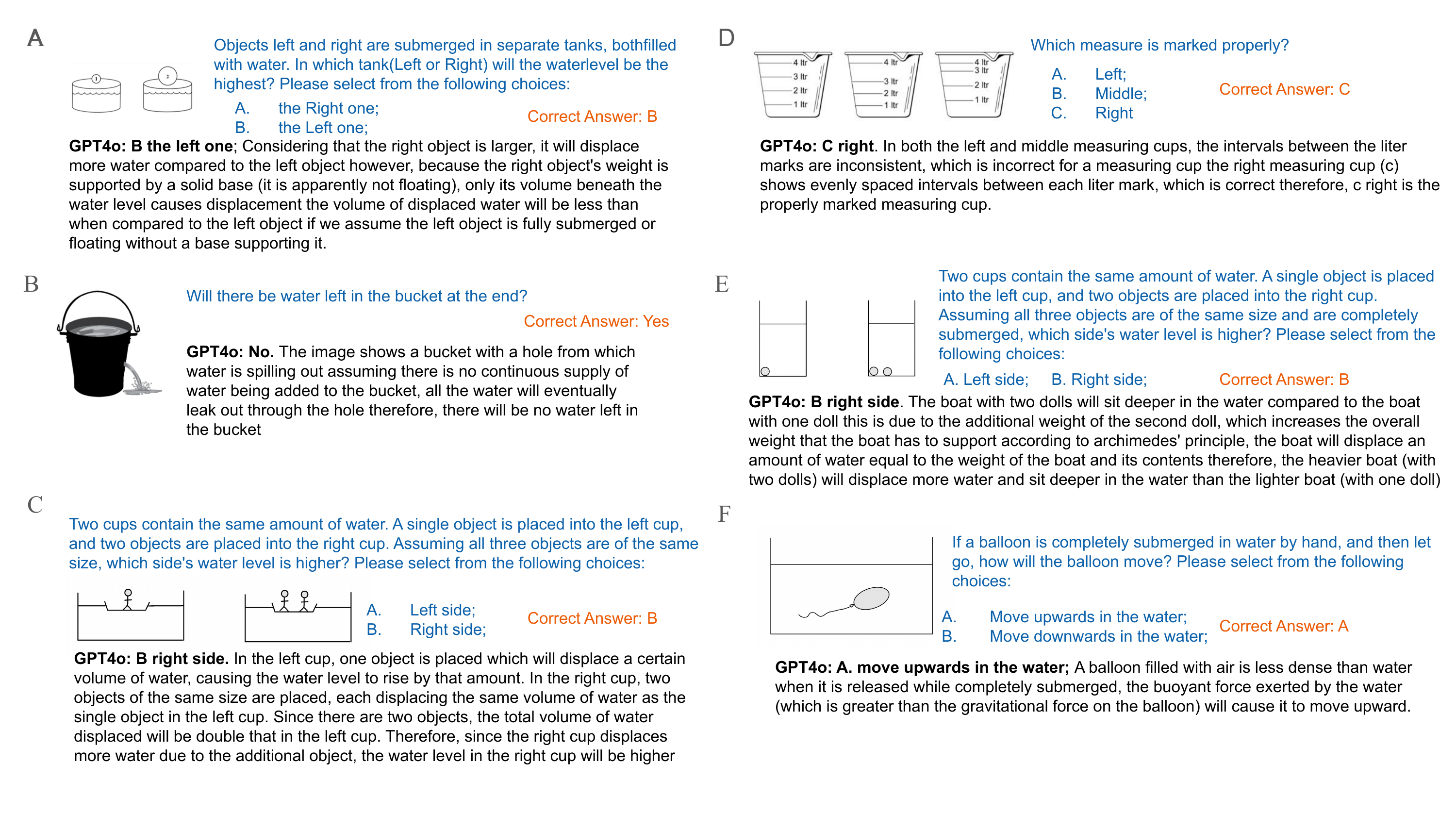 In fluid-related systems, VLMs demonstrate impressive scene understanding and detail-capturing abilities, but still face challenges with complex inference involving fluid properties.
In fluid-related systems, VLMs demonstrate impressive scene understanding and detail-capturing abilities, but still face challenges with complex inference involving fluid properties.
Key Findings
Human vs. Model Performance
Our study reveals a significant disparity between human and model performance across multiple evaluation dimensions. Humans consistently outperform models both in overall accuracy and in task-specific dimensions. These results highlight the limitations of current VLMs in replicating human-like reasoning in mechanical and intuitive physics tasks.
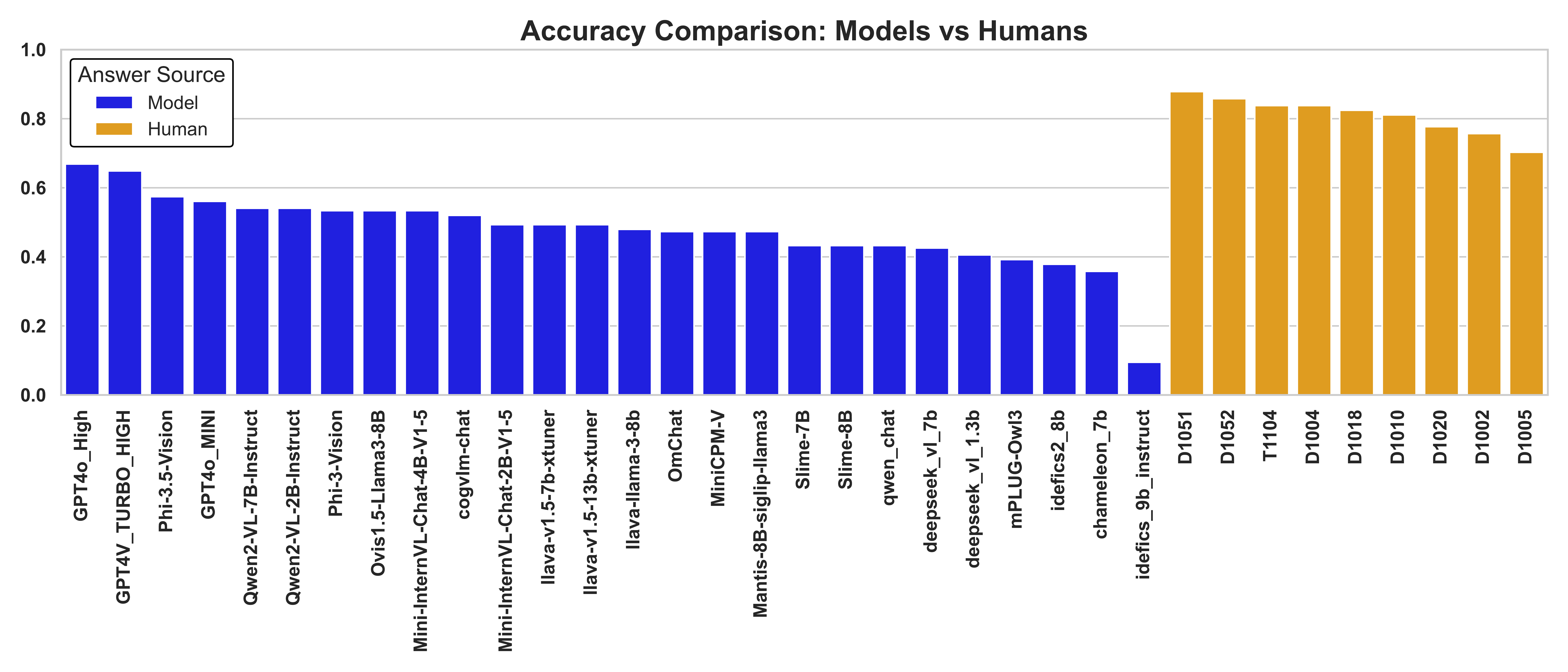 Model performance on MechBench as compared to human performance. Humans consistently outperform even the most advanced VLMs across all domains of mechanical reasoning.
Model performance on MechBench as compared to human performance. Humans consistently outperform even the most advanced VLMs across all domains of mechanical reasoning.
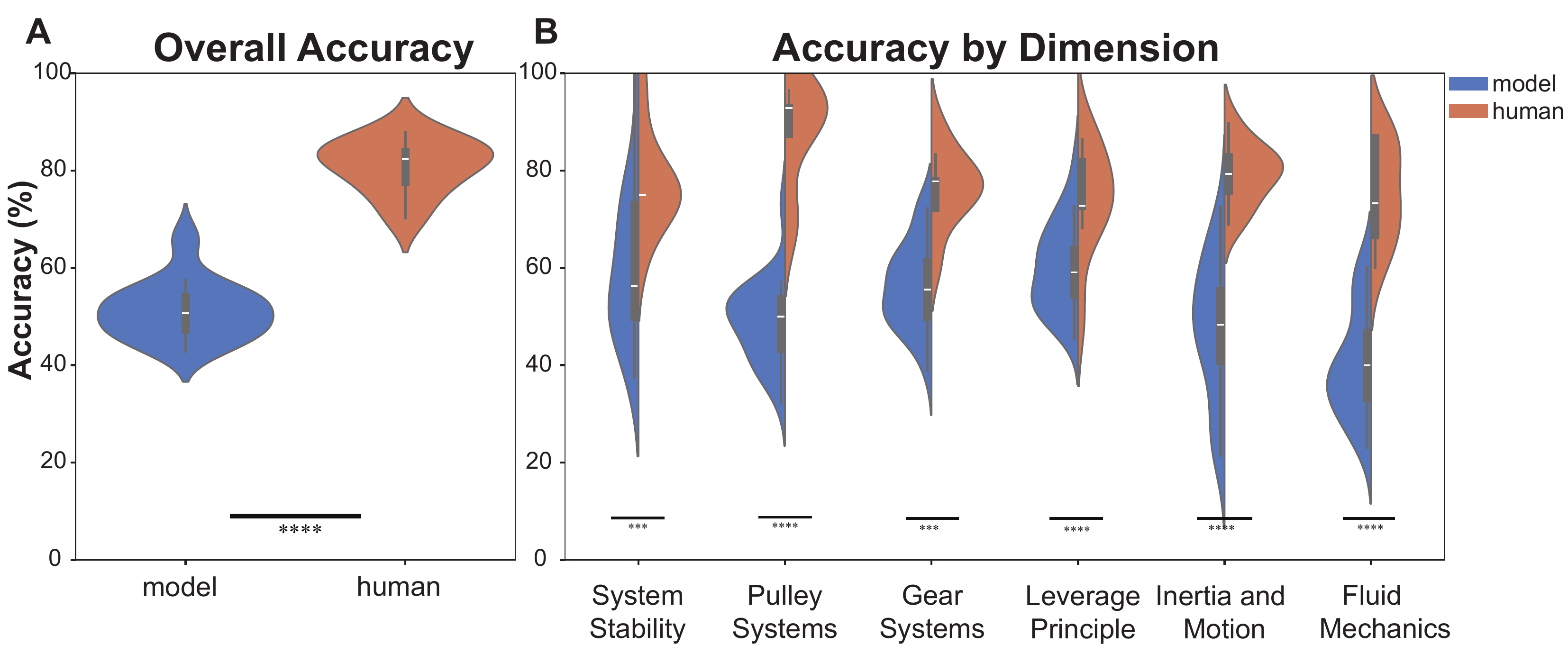 Overall and dimension-wise accuracy comparison between humans and models. Human participants consistently outperform models in each dimension (all categories p < 0.001).
Overall and dimension-wise accuracy comparison between humans and models. Human participants consistently outperform models in each dimension (all categories p < 0.001).
Model Performance and Model Size
A widely held belief in the machine learning community is that an increase in a model's scale, measured by the number of parameters, leads to systematic improvements in its reasoning abilities. However, our findings show that while model size often correlates with improved performance in many mechanical reasoning domains, some domains (specifically Gear Systems and Fluid Systems) may not benefit significantly from increased model scale.
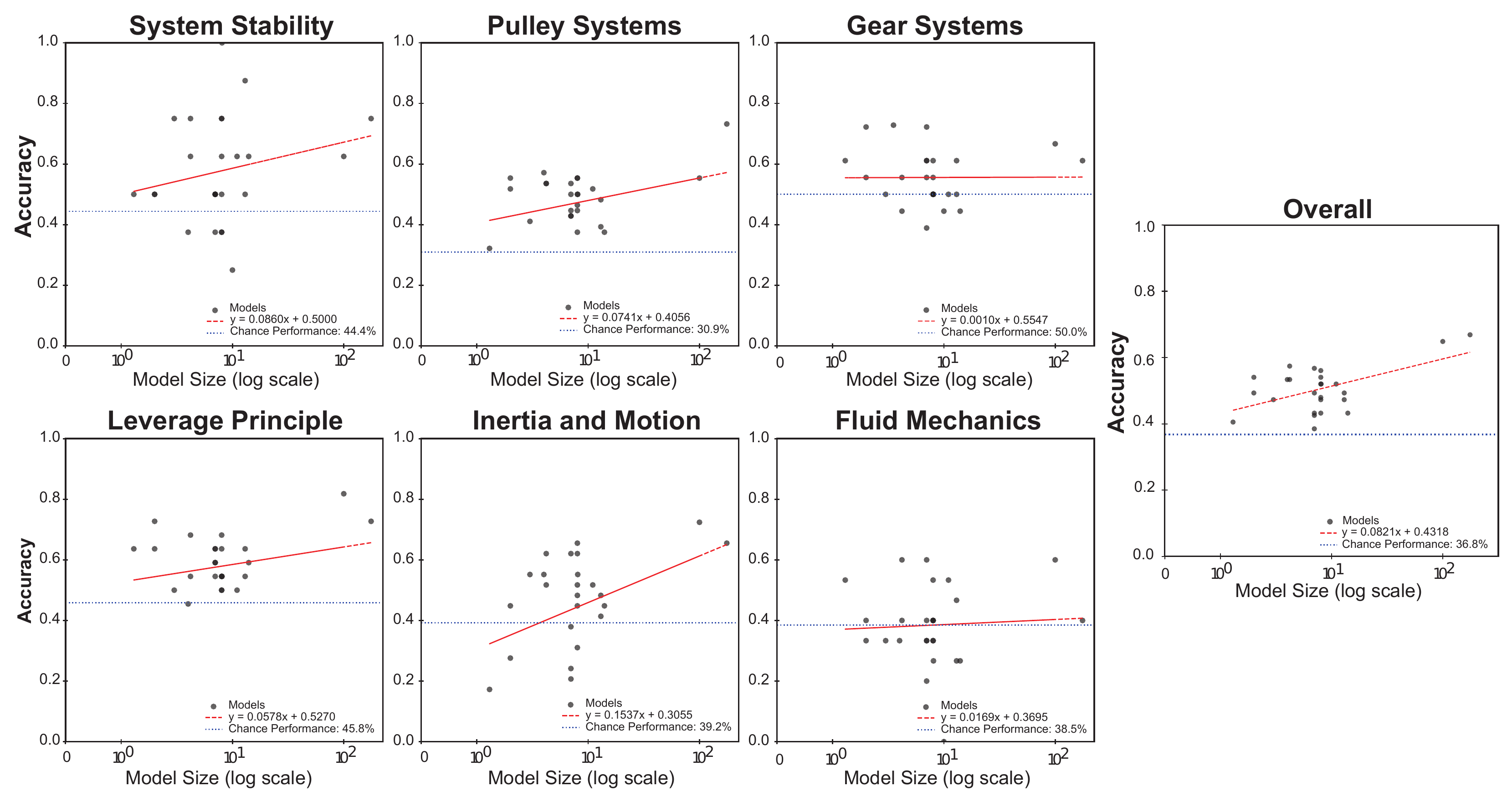 The relationship between model performance and model size. While most domains show improvement with larger models, Gear Systems and Fluid Systems show very weak relationships with model size.
The relationship between model performance and model size. While most domains show improvement with larger models, Gear Systems and Fluid Systems show very weak relationships with model size.
Conclusion
Our findings reveal that current VLMs fail to fully acquire the necessary competencies for mechanical reasoning across various domains. The observation that performance on certain tasks does not improve with increased model size underscores potential fundamental limitations in existing model architectures.
In line with previous research, we specifically highlighted model-based reasoning—the ability to mentally simulate dynamic relations within physical systems—as a potential limitation. This suggests that current VLMs may lack the ability to perform model-based reasoning, possibly highlighting a fundamental limitation in the architecture of the foundational models used in VLMs.
This work provides crucial insights into the constraints of current AI models and could inform the development of more capable architectures for mechanical reasoning tasks. Further exploration of these mechanisms could enhance our understanding of both artificial and human intelligence.